
口腔医学 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 391-396.doi: 10.13591/j.cnki.kqyx.2024.05.013
张晓婕1,刘楠1,徐子墨1,张翠2,秦青2,祝康1,任晓勇1,陈敬国1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-07-27
出版日期:2024-05-28
发布日期:2024-05-21
通讯作者:
陈敬国 E-mail:基金资助:
ZHANG Xiaojie1,LIU Nan1,XU Zimo1,ZHANG Cui2,QIN Qing2,ZHU Kang1,REN Xiaoyong1,CHEN Jingguo1( )
)
Received:2023-07-27
Online:2024-05-28
Published:2024-05-21
摘要:
近年来的研究显示,苦味受体除了在舌乳头味蕾上表达外,在呼吸、消化、生殖及心血管等非味觉系统均有不同程度的表达,具有识别苦味物质和细菌代谢产物,启动机体免疫反应,维持内环境稳态等作用。口内苦味受体的作用不仅仅是感知苦味,在牙周组织也有表达并具有相应功能,是口腔感染性疾病的潜在治疗靶点。该文总结了口内苦味受体的表达和分布情况,及其在调节口腔炎症和细菌方面的作用;探讨了苦味受体38亚型(TAS2R38)的基因多态性对先天免疫的影响,及其与龋病、牙周病易感性的关系,以期为龋病、牙周病的预防和治疗提供新思路。
中图分类号:
张晓婕, 刘楠, 徐子墨, 张翠, 秦青, 祝康, 任晓勇, 陈敬国. 口腔内苦味受体的分布和功能研究进展[J]. 口腔医学, 2024, 44(5): 391-396.
ZHANG Xiaojie, LIU Nan, XU Zimo, ZHANG Cui, QIN Qing, ZHU Kang, REN Xiaoyong, CHEN Jingguo. Progress of research on distribution and function of bitter taste receptors in oral cavity[J]. Stomatology, 2024, 44(5): 391-396.
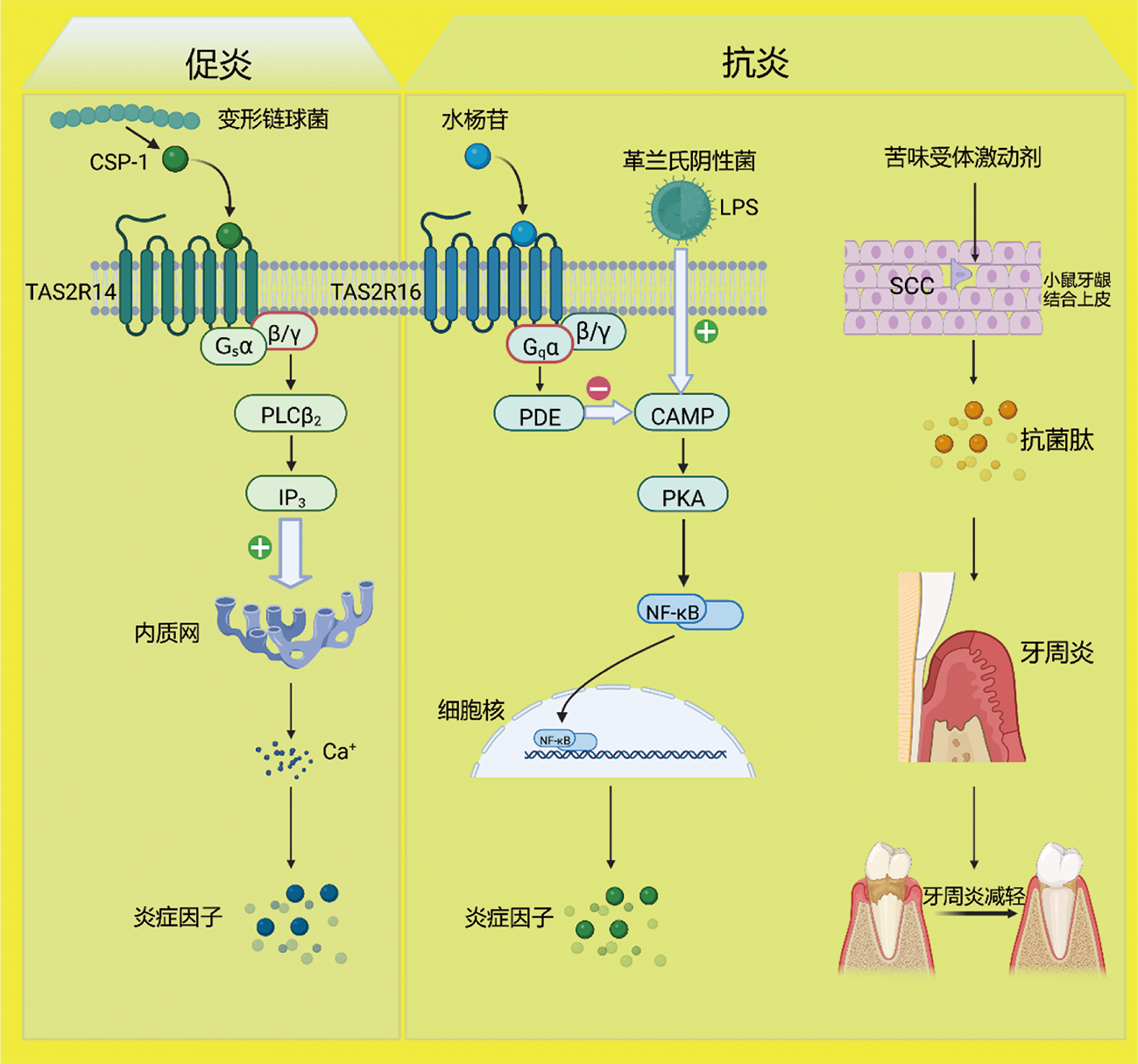
图2
苦味受体介导的口腔炎症性反应的过程机制图(绘图软件:BioRender) AMP:adenosine mono phosphate,腺苷酸;cAMP:cyclic adenosine monophosphate,环磷酸腺苷;CSP-1:competence-stimulating peptides-1,感受态刺激肽;LPS:lipopolysaccharide,脂多糖;NF-κB:nuclear factor-kappa B,核转录因子kappa B;PDE:phosphodiesterase,磷酸二酯酶;PKA:protein kinase A,蛋白激酶A;SCC:solitary chemosensory cell,孤立化学感觉细胞;PLCβ2:phospholipase Cβ2,磷脂酶Cβ2;IP3:inositol triphosphate,三磷酸肌醇;Gsα、Gqα、β/γ:G蛋白的亚基。"
| [1] |
Witt M. Anatomy and development of the human taste system[J]. Handb Clin Neurol, 2019, 164: 147-171.
doi: B978-0-444-63855-7.00010-1 pmid: 31604544 |
| [2] | Kinnamon SC, Finger TE. Recent advances in taste transduction and signaling[J]. F1000Research, 2019, 8: F1000FacultyRev-F1000Faculty2117. |
| [3] | Kooistra AJ, Mordalski S, Pándy-Szekeres G, et al. GPCRdb in 2021: Integrating GPCR sequence, structure and function[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2021, 49(D1):D335-D343. |
| [4] |
Xu WX, Wu LJ, Liu SH, et al. Structural basis for strychnine activation of human bitter taste receptor TAS2R46[J]. Science, 2022, 377(6612):1298-1304.
doi: 10.1126/science.abo1633 pmid: 36108005 |
| [5] | Jeruzal-Świᶏtecka J, Fendler W, Pietruszewska W. Clinical role of extraoral bitter taste receptors[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(14):5156. |
| [6] |
Howitt MR, Lavoie S, Michaud M, et al. Tuft cells, taste-chemosensory cells, orchestrate parasite type 2 immunity in the gut[J]. Science, 2016, 351(6279):1329-1333.
doi: 10.1126/science.aaf1648 pmid: 26847546 |
| [7] | Lee RJ, Hariri BM, McMahon DB, et al. Bacterial d-amino acids suppress sinonasal innate immunity through sweet taste receptors in solitary chemosensory cells[J]. Sci Signal, 2017, 10(495):eaam7703. |
| [8] | Xi R, Zheng X, Tizzano M. Role of taste receptors in innate immunity and oral health[J]. J Dent Res, 2022, 101(7):759-768. |
| [9] | 覃凯华, 贾雨鑫, 张文博, 等. 苦味觉信息的感受、传递和调控机制[J]. 神经解剖学杂志, 2021, 37(3):342-346. |
| [10] | Nguyen QT, Beck Coburn GE, Valentino A, et al. Mouse mandibular retromolar taste buds associated with a mucus salivary gland[J]. Chem Senses, 2021, 46: bjab019. |
| [11] |
Manson ML, Säfholm J, Al-Ameri M, et al. Bitter taste receptor agonists mediate relaxation of human and rodent vascular smooth muscle[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2014, 740: 302-311.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.07.005 pmid: 25036266 |
| [12] |
Dalesio NM, Barreto Ortiz SF, Pluznick JL, et al. Olfactory, taste, and photo sensory receptors in non-sensory organs: It just makes sense[J]. Front Physiol, 2018, 9: 1673.
doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01673 pmid: 30542293 |
| [13] | Liu X, Gu F, Jiang L, et al. Expression of bitter taste receptor Tas2r105 in mouse kidney[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2015, 458(4):733-738. |
| [14] |
Foster SR, Blank K, See Hoe LE, et al. Bitter taste receptor agonists elicit G-protein-dependent negative inotropy in the murine heart[J]. FASEB J, 2014, 28(10):4497-4508.
doi: 10.1096/fj.14-256305 pmid: 25002118 |
| [15] |
Zagorchev P, Petkov GV, Gagov HS. Bitter taste receptors as regulators of abdominal muscles contraction[J]. Physiol Res, 2019, 68(6):991-995.
pmid: 31647294 |
| [16] |
Lee RJ, Cohen NA. Taste receptors in innate immunity[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2015, 72(2):217-236.
doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1736-7 pmid: 25323130 |
| [17] | Medapati MR, Bhagirath AY, Singh N, et al. Bitter taste receptor T2R14 modulates gram-positive bacterial internalization and survival in gingival epithelial cells[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(18):9920. |
| [18] | Zhou ZY, Xi RH, Liu JX, et al. TAS2R16 activation suppresses LPS-induced cytokine expression in human gingival fibroblasts[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 726546. |
| [19] | Rowan NR, Soler ZM, Othieno F, et al. Impact of bitter taste receptor phenotype upon clinical presentation in chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2018, 8(9):1013-1020. |
| [20] | Medapati MR, Singh N, Bhagirath AY, et al. Bitter taste receptor T2R14 detects quorum sensing molecules from cariogenic Streptococcus mutans and mediates innate immune responses in gingival epithelial cells[J]. FASEB J, 2021, 35(3):e21375. |
| [21] |
Zheng X, Tizzano M, Redding K, et al. Gingival solitary chemosensory cells are immune sentinels for periodontitis[J]. Nat Commun, 2019, 10(1):4496.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12505-x pmid: 31582750 |
| [22] |
Giuliani C, Franceschi C, Luiselli D, et al. Ecological sensing through taste and chemosensation mediates inflammation: A biological anthropological approach[J]. Adv Nutr, 2020, 11(6):1671-1685.
doi: 10.1093/advances/nmaa078 pmid: 32647890 |
| [23] |
Cattaneo C, Gargari G, Koirala R, et al. New insights into the relationship between taste perception and oral microbiota composition[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1):3549.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-40374-3 pmid: 30837660 |
| [24] | Welcome MO, Mastorakis NE. The taste of neuroinflammation: Molecular mechanisms linking taste sensing to neuroinflammatory responses[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2021, 167: 105557. |
| [25] |
Saunders CJ, Christensen M, Finger TE, et al. Cholinergic neurotransmission links solitary chemosensory cells to nasal inflammation[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2014, 111(16):6075-6080.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1402251111 pmid: 24711432 |
| [26] | Kim D, Cho S, Castaño MA, et al. Biased TAS2R bronchodilators inhibit airway smooth muscle growth by downregulating phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2[J]. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2019, 60(5):532-540. |
| [27] | Kaur K, Turner A, Jones P, et al. A cross-sectional study of bitter-taste receptor genotypes, oral health, and markers of oral inflammation[J]. Oral, 2021, 1(2):122-138. |
| [28] | Alharbi KS, Fuloria NK, Fuloria S, et al. Nuclear factor-kappa B and its role in inflammatory lung disease[J]. Chem Biol Interact, 2021, 345: 109568. |
| [29] |
Tran HTT, Herz C, Ruf P, et al. Human T2R38 bitter taste receptor expression in resting and activated lymphocytes[J]. Front Immunol, 2018, 9: 2949.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02949 pmid: 30619309 |
| [30] |
Gil S, Coldwell S, Drury JL, et al. Genotype-specific regulation of oral innate immunity by T2R38 taste receptor[J]. Mol Immunol, 2015, 68(2 Pt C):663-670.
doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2015.10.012 pmid: 26552761 |
| [31] |
Chamoun E, Mutch DM, Allen-Vercoe E, et al. A review of the associations between single nucleotide polymorphisms in taste receptors, eating behaviors, and health[J]. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, 2018, 58(2):194-207.
doi: 10.1080/10408398.2016.1152229 pmid: 27247080 |
| [32] | Chamoun E, Carroll NA, Duizer LM, et al. The relationship between single nucleotide polymorphisms in taste receptor genes, taste function and dietary intake in preschool-aged children and adults in the Guelph family health study[J]. Nutrients, 2018, 10(8):990. |
| [33] | 陆洋宇, 席苒珲, 郑欣, 等. 味觉受体信号转导机制及对微生物的调控[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2017, 35(5):549-554. |
| [34] |
Wendell S, Wang X, Brown M, et al. Taste genes associated with dental caries[J]. J Dent Res, 2010, 89(11):1198-1202.
doi: 10.1177/0022034510381502 pmid: 20858777 |
| [35] |
Pidamale R, Sowmya B, Thomas A, et al. Genetic sensitivity to bitter taste of 6-n Propylthiouracil: A useful diagnostic aid to detect early childhood caries in pre-school children[J]. Indian J Hum Genet, 2012, 18(1):101-105.
doi: 10.4103/0971-6866.96672 pmid: 22754231 |
| [36] |
Shimomura-Kuroki J, Nashida T, Miyagawa Y, et al. The role of genetic factors in the outbreak mechanism of dental caries[J]. J Clin Pediatr Dent, 2018, 42(1):32-36.
doi: 10.17796/1053-4628-42.1.6 pmid: 28937897 |
| [37] | Kiliç M, Gurbuz T, Kahraman CY, et al. Relationship between the TAS2R38 and TAS1R2 polymorphisms and the dental status in obese children[J]. Dent Med Probl, 2022, 59(2):233-240. |
| [38] |
Khimsuksri S, Paphangkorakit J, Pitiphat W, et al. TAS2R38 polymorphisms and oral diseases in Thais: A cross-sectional study[J]. BMC Oral Health, 2022, 22(1):21.
doi: 10.1186/s12903-022-02043-2 pmid: 35090440 |
| [39] | 周学东. 牙体牙髓病学[M]. 5版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2020. |
| [40] |
Shetty V, Pooja BL, Hegde AM. PROP test: Prediction of caries risk by genetic taste perception among the visually impaired children[J]. Spec Care Dentist, 2014, 34(1):34-40.
doi: 10.1111/j.1754-4505.2012.00307.x pmid: 24382369 |
| [41] | Yeomans MR, Vi C, Mohammed N, et al. Re-evaluating how sweet-liking and PROP-tasting are related[J]. Physiol Behav, 2022, 246: 113702. |
| [42] | Cecati M, Vignini A, Borroni F, et al. TAS1R3 and TAS2R38 polymorphisms affect sweet taste perception: An observational study on healthy and obese subjects[J]. Nutrients, 2022, 14(9):1711. |
| [43] |
Kinane DF, Stathopoulou PG, Papapanou PN. Periodontal diseases[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2017, 3: 17038.
doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2017.38 pmid: 28805207 |
| [44] |
Lee RJ, Kofonow JM, Rosen PL, et al. Bitter and sweet taste receptors regulate human upper respiratory innate immunity[J]. J Clin Invest, 2014, 124(3):1393-1405.
doi: 10.1172/JCI72094 pmid: 24531552 |
| [45] | Cheng W, Yao MY, Liu FN. Bitter taste receptor as a therapeutic target in orthopaedic disorders[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2021, 15: 895-903. |
| [46] | 周佳佳, 赵蕾, 徐欣. 牙周炎相关基因多态性的研究进展[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2022, 49(4):432-440. |
| [47] |
Finger TE, Böttger B, Hansen A, et al. Solitary chemoreceptor cells in the nasal cavity serve as sentinels of respiration[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2003, 100(15):8981-8986.
pmid: 12857948 |
| [1] | 宋野, 任银婷, 张轶涵, 韩晶莹. 不同拔牙方式对骨性Ⅱ类错牙合畸形Bolton指数及咬合关系的影响[J]. 口腔医学, 2024, 44(5): 334-337. |
| [2] | 李颖, 潘丹, 周瑜. 血液系统肿瘤口腔表征[J]. 口腔医学, 2024, 44(5): 386-390. |
| [3] | 田野, 石晓璐, 王济朋, 翟少博, 刘洋, 杨征, 吴毓川, 储顺礼. 钛网植骨联合上颌窦底提升术改善上颌磨牙区严重骨缺损病例1例[J]. 口腔医学, 2024, 44(4): 287-291. |
| [4] | 孙昕奕, 潘玥彤, 陆欣悦, 吕中静, 袁健, 李家锋, 石欢. PTK7在口腔鳞癌中的表达分析及其生物学功能研究[J]. 口腔医学, 2024, 44(4): 268-275. |
| [5] | 沈梦圆, 张雪莹, 徐欣晨, 李晓东, 孟箭. 口腔癌游离皮瓣移植术后谵妄的相关因素及影响研究[J]. 口腔医学, 2024, 44(4): 261-267. |
| [6] | 崔鸢, 刘晓燕, 魏娇, 刘杨, 刘青. 透析相关舌淀粉样变1例[J]. 口腔医学, 2024, 44(3): 200-202. |
| [7] | 张亮亮, 古建昌, 刘云, 王晓岚, 柳云霞. 1990—2019年中国归因于饮酒的口腔癌死亡趋势及年龄-时期-队列模型分析[J]. 口腔医学, 2024, 44(3): 177-183. |
| [8] | 万锦波, 钱一言, 王羽立, 肖娜, 卞一峰, 杜一飞. 经侧方颈纹入路行选择性颈淋巴结清扫术的临床初探[J]. 口腔医学, 2024, 44(3): 173-176. |
| [9] | 王涵, 胡建. 种植修复数字化印模准确性影响因素的研究进展[J]. 口腔医学, 2024, 44(3): 221-226. |
| [10] | 张夏桐, 吴文治, 陈卓. 单细胞测序和空间转录组技术在口腔医学的应用进展[J]. 口腔医学, 2024, 44(3): 214-221. |
| [11] | 王亚培, 罗玉春, 刘为, 刘畅, 唐婉容. EP300对口腔鳞癌细胞增殖和迁移的影响[J]. 口腔医学, 2024, 44(2): 88-93. |
| [12] | 王伟娜, 雒静, 赵金花, 李泽彬, 李潇. 三维打印口腔修复种植体的研究进展[J]. 口腔医学, 2024, 44(2): 156-160. |
| [13] | 库得来提·阿不都克力木, 董红宾, 多力昆·吾甫尔. 壳聚糖温敏水凝胶在口腔相关组织工程的应用进展[J]. 口腔医学, 2024, 44(2): 139-143. |
| [14] | 蒲奕名, 周静, 刘清辉, 吕红, 卜鸿鹄, 李倩, 唐荣穗. 数字化导板引导下拔除上颌埋伏牙后同期种植1例[J]. 口腔医学, 2024, 44(2): 121-125. |
| [15] | 虞颖娟, 朱文卿. 种植体中央螺丝扭矩衰减的回顾性临床研究[J]. 口腔医学, 2024, 44(1): 41-45. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 苏公网安备32010602011670号
苏公网安备32010602011670号